EHC-MM
Embodied Holistic Control for Mobile Manipulation

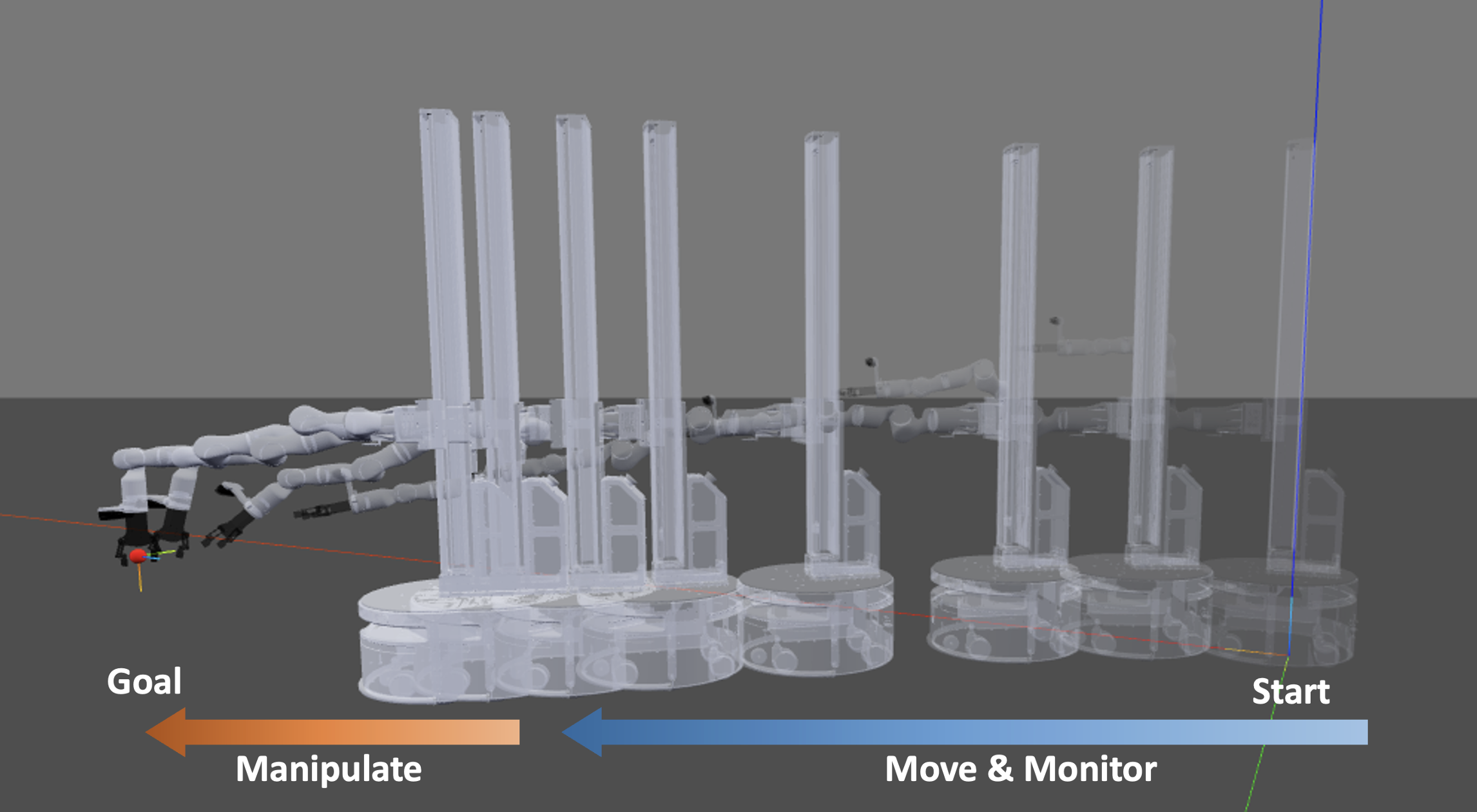
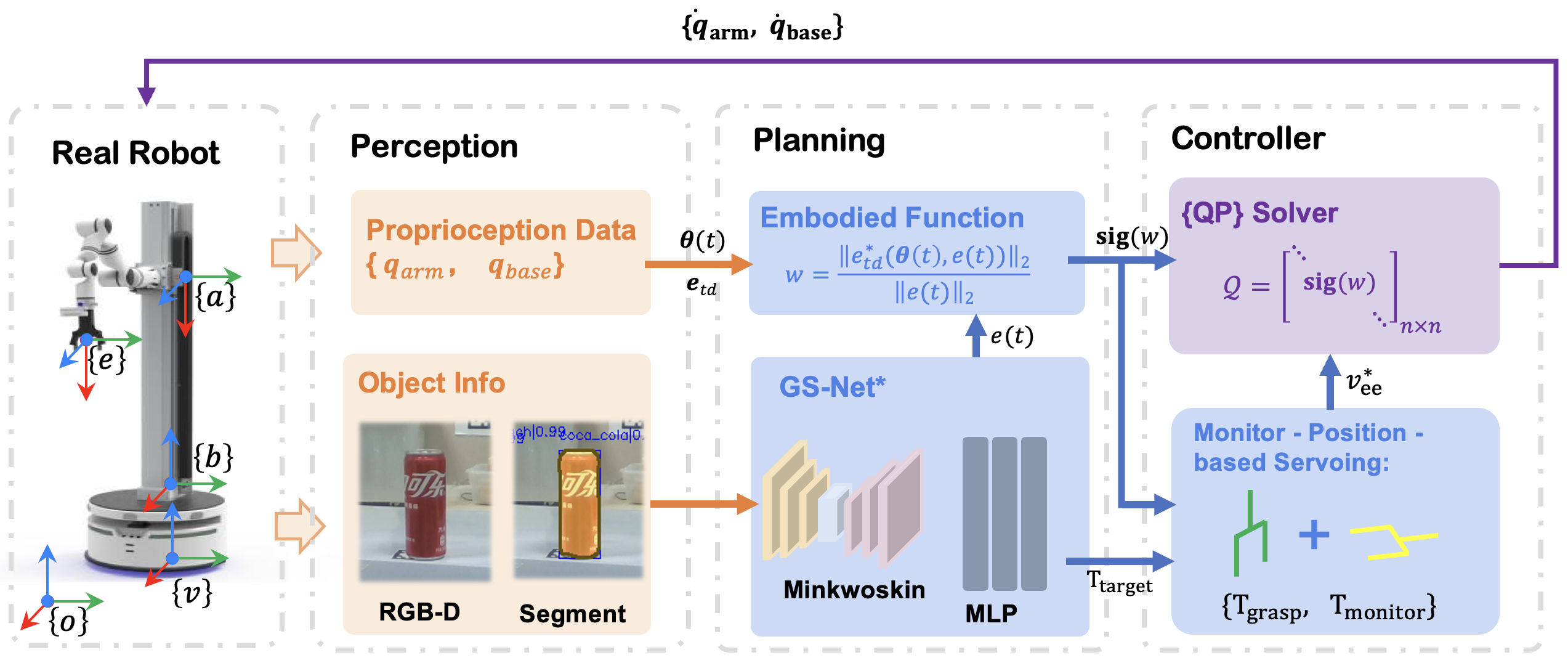
Mobile manipulation typically entails the base for mobility, the arm for accurate manipulation, and the camera for perception. It is necessary to follow the principle of Distant Mobility, Close Grasping (DMCG) in holistic control. We propose Embodied Holistic Control for Mobile Manipulation (EHC-MM) with the embodied function of sig(w): By formulating the DMCG principle as a Quadratic Programming (QP) problem, sig(w) dynamically balances the robot’s emphasis between movement and manipulation, considering the robot’s state and environment. In addition, we propose the Monitor-Position-Based Servoing (MPBS) with sig(w), enabling the tracking of the target during the operation. This approach allows coordinated control between the robot’s base, arm, and camera. Through extensive simulations and real-world experiments, our approach significantly improves both the success rate and efficiency of mobile manipulation tasks, achieving a 95.6% success rate in real-world scenarios and a 52.8% increase in time efficiency.
Video
Reference
If you find our work useful, please cite:
@misc{wang2025ehcmmembodiedholisticcontrol,
title={EHC-MM: Embodied Holistic Control for Mobile Manipulation},
author={Jiawen Wang and Yixiang Jin and Jun Shi and Yong A and Dingzhe Li and Fuchun Sun and Dingsheng Luo and Bin Fang},
year={2025},
eprint={2409.08527},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.RO},
url={https://arxiv.org/abs/2409.08527}
}